Loop Node
Loop nodes allow you to iterate through each element in an array and apply transformations or operations to them. They work similarly to JavaScript’s map() function, taking an array as input and outputting a processed array.
Overview
Loop nodes create a sub-workflow that executes once for each item in the input array. Each iteration processes one array element and produces a corresponding output element, maintaining the same array structure.
How Loops Work
You can think of loop nodes as JavaScript’s ["x","y"].map() function:
- Input: An array of values
- Processing: Each array element is processed through a sub-workflow
- Output: A new array where each element corresponds to the processed result
Loop nodes contain an embedded sub-workflow consisting of two required nodes:
- Start Loop Once - The entry point for each loop cycle
- End Loop Once - The exit point that defines the output of each iteration
Sub-Workflow Structure
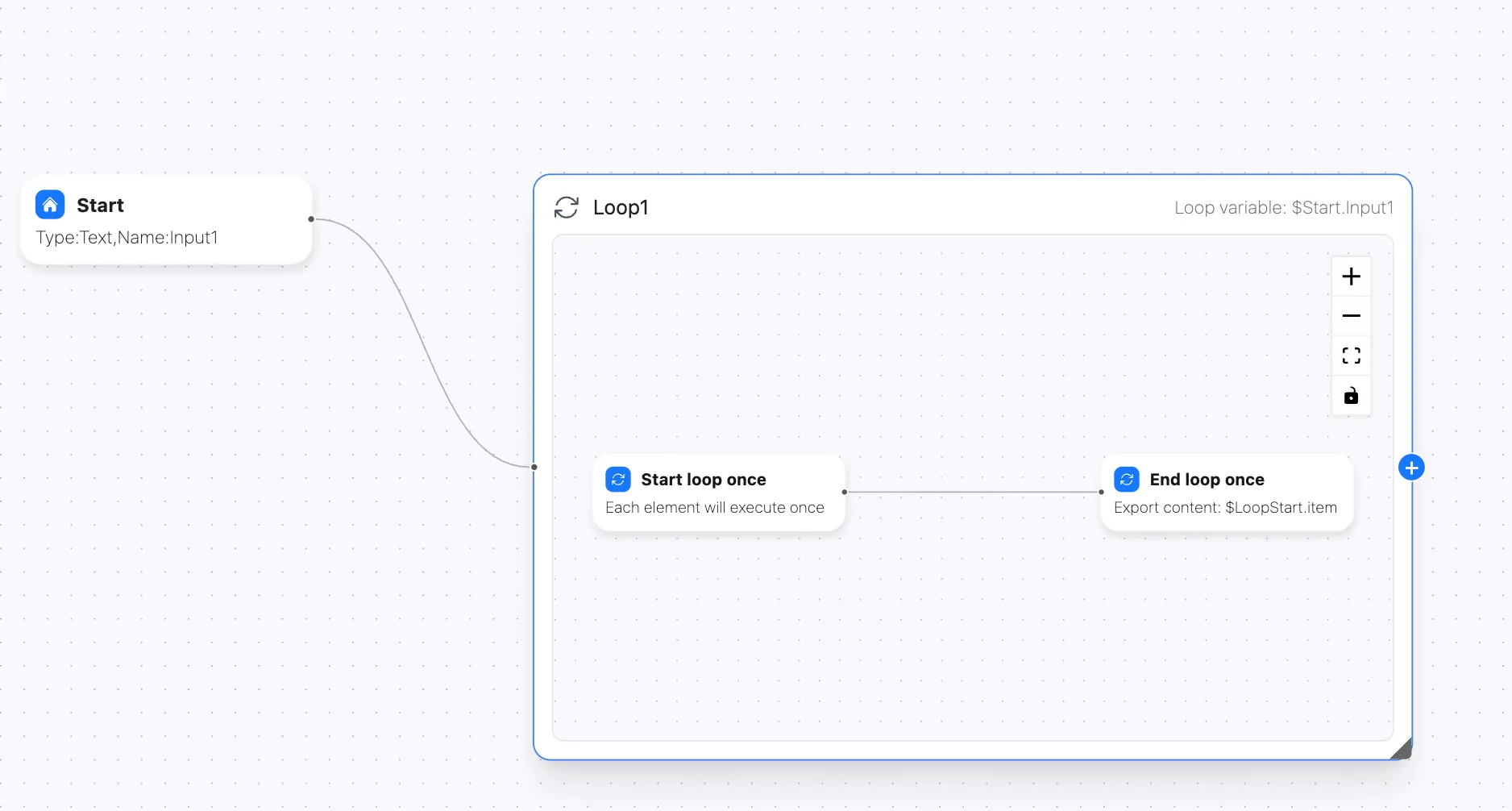
Each loop node contains:
Start Loop Once Node
This node provides two variables for each iteration:
$loopStart.item- The value of the current array element$loopStart.index- The index of the current array element (starting from 0)
End Loop Once Node
This node determines what is returned from each iteration. The value exported by this node will become the corresponding element in the output array.
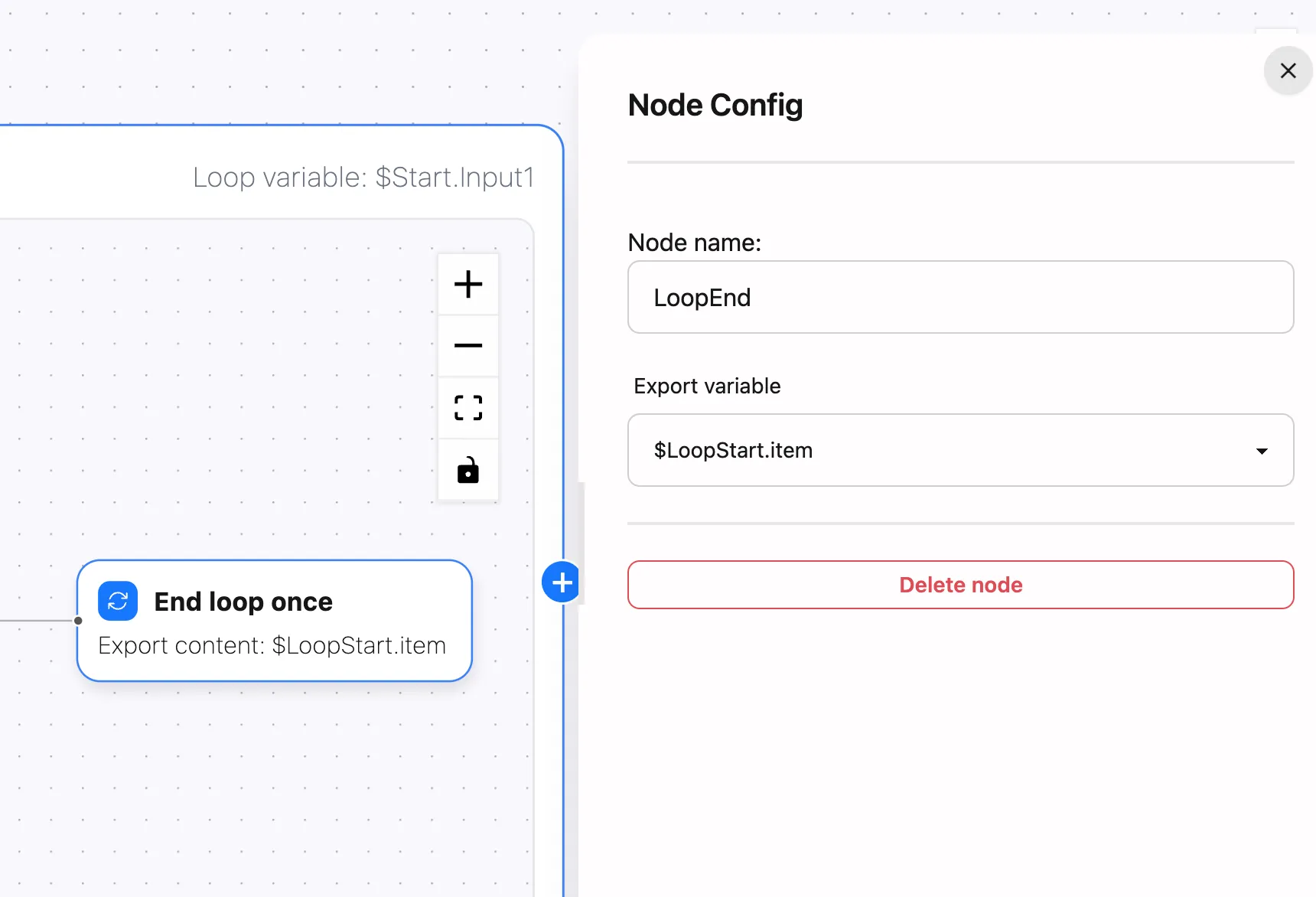
Configure the data to be exported from each iteration. The selected output variable determines the content in the final result array.
Configuration Instructions
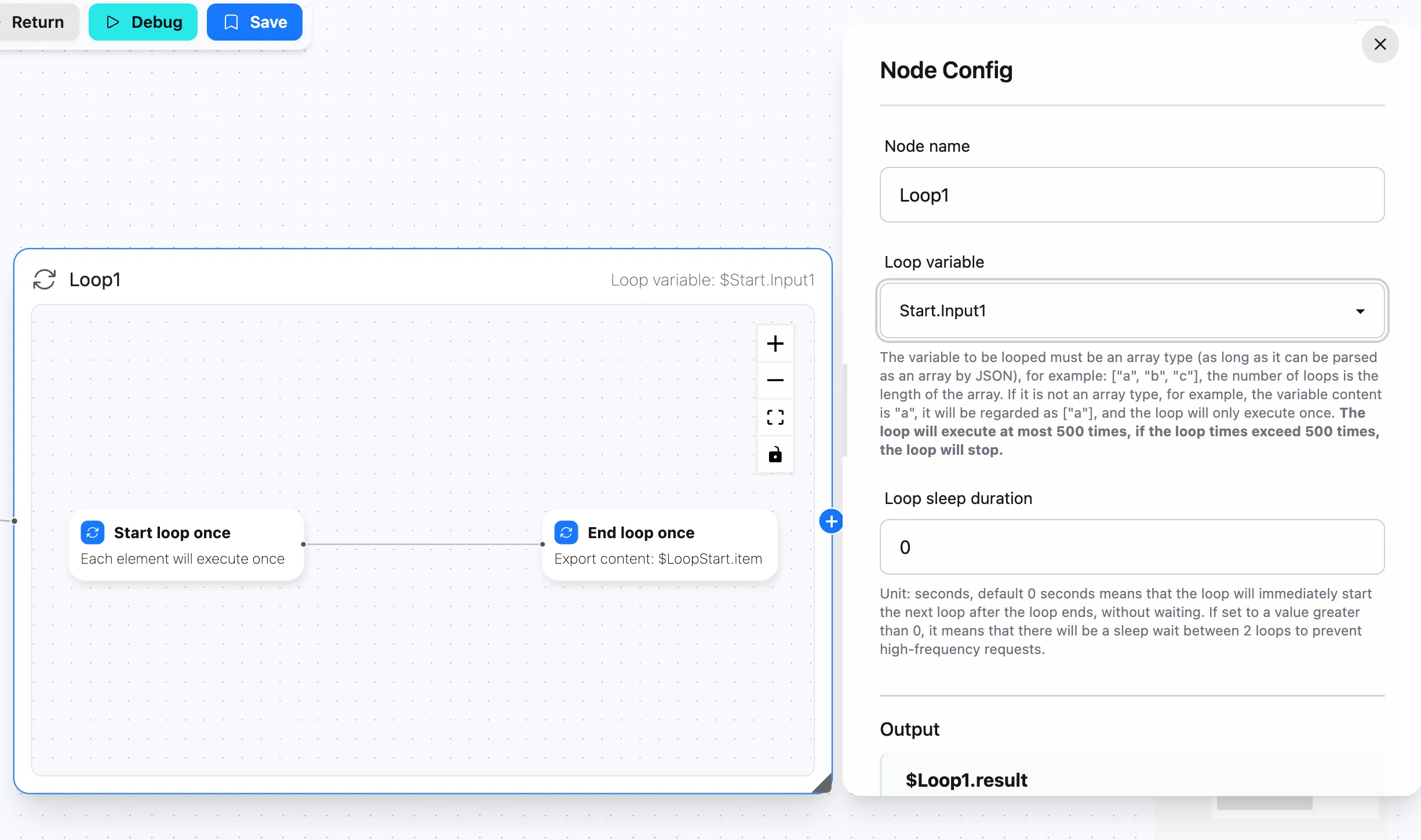
Node Name
Set a descriptive name for your loop operation.
Loop Variable
Select the variable containing the array to iterate over. The variable must be:
- Array type (can be parsed as a JSON array)
- For example:
["a", "b", "c"]will iterate 3 times - Non-array type values will be treated as single-element arrays
Loop Interval
Set the delay time between iterations in seconds. Defaults to 0 (no delay).
Output
The loop node outputs $loop1.result - an array containing the results of each iteration.
Usage Examples
1. Text Processing
Process a string array, applying transformations to each string:
- Input:
["hello", "world", "flowai"] - Sub-workflow: Convert to uppercase
- Output:
["HELLO", "WORLD", "FLOWAI"]
2. Data Enrichment
Enhance array data with additional information:
- Input:
[{"id": 1}, {"id": 2}, {"id": 3}] - Sub-workflow: Get user details for each ID
- Output:
[{"id": 1, "name": "John"}, {"id": 2, "name": "Jane"}, ...]
3. API Batch Processing
Make multiple API calls with different parameters:
- Input:
["product1", "product2", "product3"] - Sub-workflow: Get price for each product
- Output:
[99.99, 149.99, 79.99]
Best Practices
- Performance: Be aware of the loop count limit (maximum 500 iterations)
- Rate Limiting: Use loop intervals when making external API calls
- Error Handling: Consider how to handle failures in individual iterations
- Data Types: Ensure loop variables are properly formatted as arrays
- Output Structure: Plan the data structure needed by the End Loop Once node
Common Patterns
Simple Value Transformation
Use when you need to transform each array element:
- Configure End Loop Once to output the transformed value
- Maintain the same array structure
Data Aggregation
Use when you need to collect information from each element:
- Configure End Loop Once to output enriched objects
- Combine original data with newly computed data
Filtering with Processing
Combine with conditional nodes to selectively process array elements:
- Use conditionals in the sub-workflow
- Output different values based on conditions
Need a Custom AI Agent?
Custom AI agents designed for real-world business operations.
