LLM Agent Node
The LLM Agent node is a core component within the FlowAI Smart Workflow system. It can autonomously select and combine tools during execution to complete complex multi-step tasks. The latest version of the Agent has been fully integrated with the workflow_worker execution engine, supporting sub-workflow toolification, MCP extensions, and more robust built-in tool capabilities.
Core Upgrade Highlights
- Sub-workflow Toolification: Any workflow can be registered as an Agent tool. The system automatically generates unique aliases, synchronizes names and descriptions, and constructs JSON Schema based on input nodes, ensuring standardized invocation in prompts.
- Enhanced MCP Integration: The frontend supports adding multiple types of MCP servers (
sse/streamable-http) and configuring custom headers. The Worker validates all MCP tool JSON Schemas one by one and returns detailed error messages. - Extended Built-in Tools: New additions include Markdown-to-Excel, URL encoding, Base64, hash, and time tools, supporting direct combination in prompts.
- Multi-language & Streaming Feedback: System Prompt automatically injects the specified response language. During execution, iteration rounds, reasoning processes, and tool call statuses are streamed back in real-time for convenient Agent behavior monitoring.
Node Configuration Overview
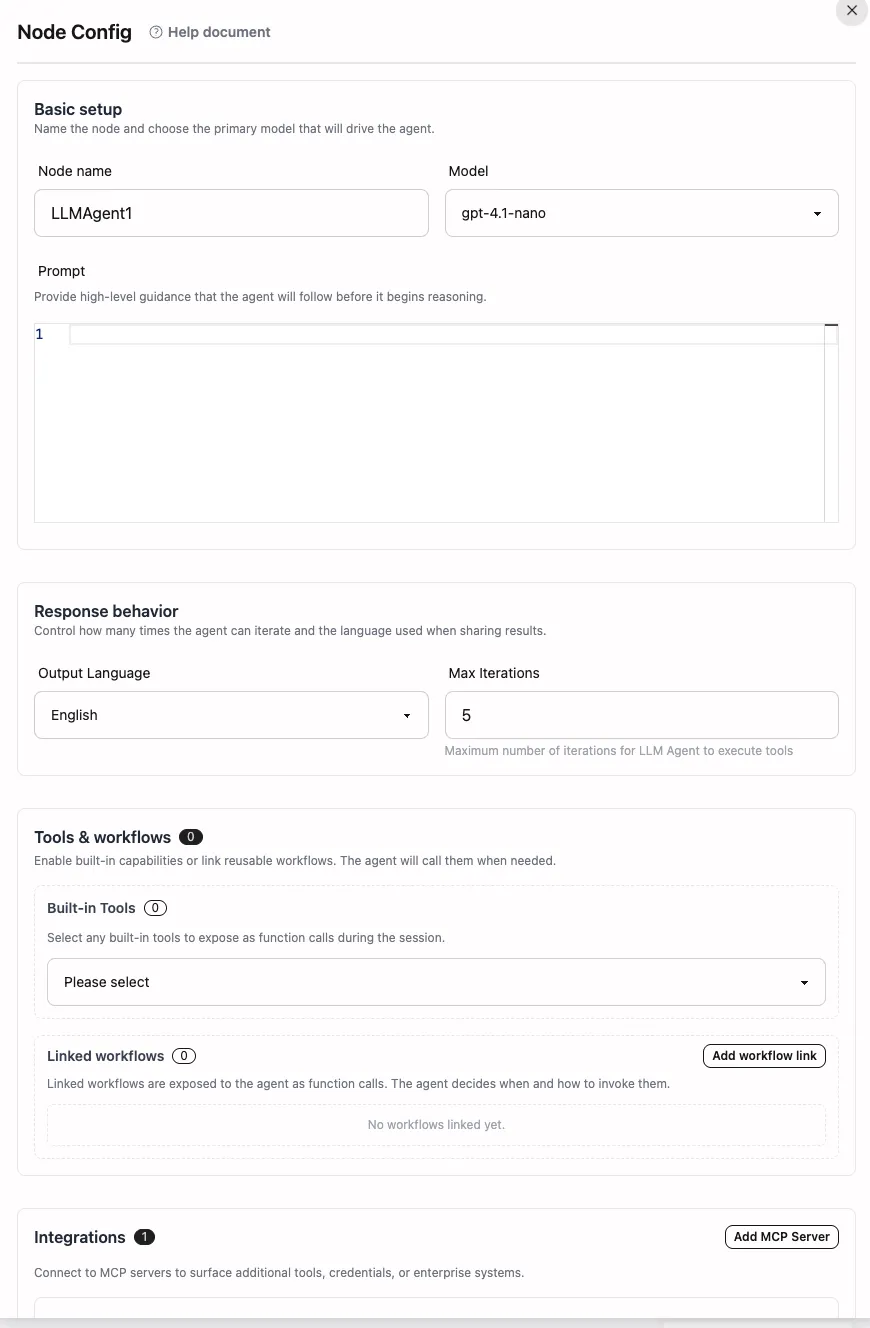
Basic Settings
- Node Name: Affects variable references, for example:
$LLMAgent1.result→$IntelligentAssistant.result. We recommend using semantically clear names to facilitate team collaboration. - Model Selection: The dropdown integrates official models and “My Models”, automatically filtering out models that don’t support Function Calling. You can balance performance and cost based on task requirements.
- Prompt Editor: Supports variable injection, multi-step task descriptions, and output format definitions.
Response & Execution Control
- Output Language: Selected from the frontend and injected into System Prompt. The Worker reminds the model to always output the final answer in the specified language.
- Maximum Iteration Rounds: Controls how many times the Agent can loop through tool calls, default is 5, maximum is 50. Each round may include multiple tool calls and reasoning steps. Exceeding the limit returns an error message.
Tools & Integrations
- Built-in Tool Selection: Check boxes to enable the Agent to call official tools (see “Built-in Tool Capabilities” below). Enabling more tools increases model trial costs, so streamline as needed.
- Linked Workflows: Click “Add Linked Workflow” to bind other workflows. The frontend automatically generates secure aliases and displays input fields.
- MCP Servers: Supports configuring multiple MCP endpoints, including name, type, URL, and custom headers. The Worker validates schemas in
connectMCPServerbefore attempting connections, returning itemized errors when failures occur for easier troubleshooting.
LLM Agent vs LLM Node
| Feature | LLM Agent Node | LLM Node |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Intelligent agent with autonomous decision-making and tool calling | Single AI inference for text generation |
| Tool Calling | Supports automatic calling of multiple tools | Does not support tool calling |
| Task Complexity | Suitable for complex, multi-step tasks | Suitable for single text generation tasks |
| Autonomy | High, can autonomously select tools based on tasks | Low, strictly follows prompts |
| Use Cases | Data collection, analysis, automated processing | Content generation, text analysis |
Prompt Writing Tips
Compared to LLM nodes, LLM Agent prompts focus more on task objectives, success criteria, and tool usage constraints. When linked workflows or MCP tools are enabled, explicitly inform the Agent of tool purposes and trigger conditions in the prompt, for example:
When you need to generate a daily report draft, call the report_generator tool with {"date": "$input.date"}.Basic Syntax Example
Please help me query the latest information about "$input.keyword" at http://example.com and provide three key points.Multi-step Task Example
Please execute the following tasks:1. Call the fetch_web tool to scrape the quote page for "$input.stock_code"2. Use calculator to compute the average price over the past 7 days3. If the average price exceeds $input.threshold, call http_call to send an alert to the notification APIData Processing Example
Please analyze the following data: $input.data_tableRequirements:1. Output the mean and standard deviation for each column2. Use md2xls to convert the Markdown table into a downloadable XLSX link3. Provide three actionable recommendations based on findingsBuilt-in Tool Capabilities
The current version supports the following built-in tools (see workflow_worker/tools/tools.go for details):
- fetch_web: Scrapes web content, returns body text and metadata, suitable for news/price collection.
- http_call: Initiates GET/POST/PUT/DELETE requests with custom headers and body, commonly used to trigger external APIs.
- calculator: Executes complex mathematical expressions including trigonometric functions, logarithms, and constants, suitable for statistical analysis.
- md2xls: Converts Markdown content containing tables into downloadable XLSX files.
- url_codec: URL-encodes or decodes strings.
- base64_codec: Performs Base64 encoding/decoding.
- hash: Calculates
md5/sha1/sha256hash values. - now: Returns the current time in a specified timezone (RFC3339), convenient for timestamp recording.
Linked Workflow Instructions
- In the configuration panel, click “Add Linked Workflow” and select the target workflow.
- The system automatically generates a normalized alias based on the workflow name (lowercase letters, numbers, underscore/hyphen only).
- Input fields displayed on the frontend come from workflow input nodes. The Worker generates JSON Schema for these fields for LLM reference.
If a sub-workflow execution fails, the Agent receives an error message and can decide whether to continue with the next step.
MCP Integration Guide
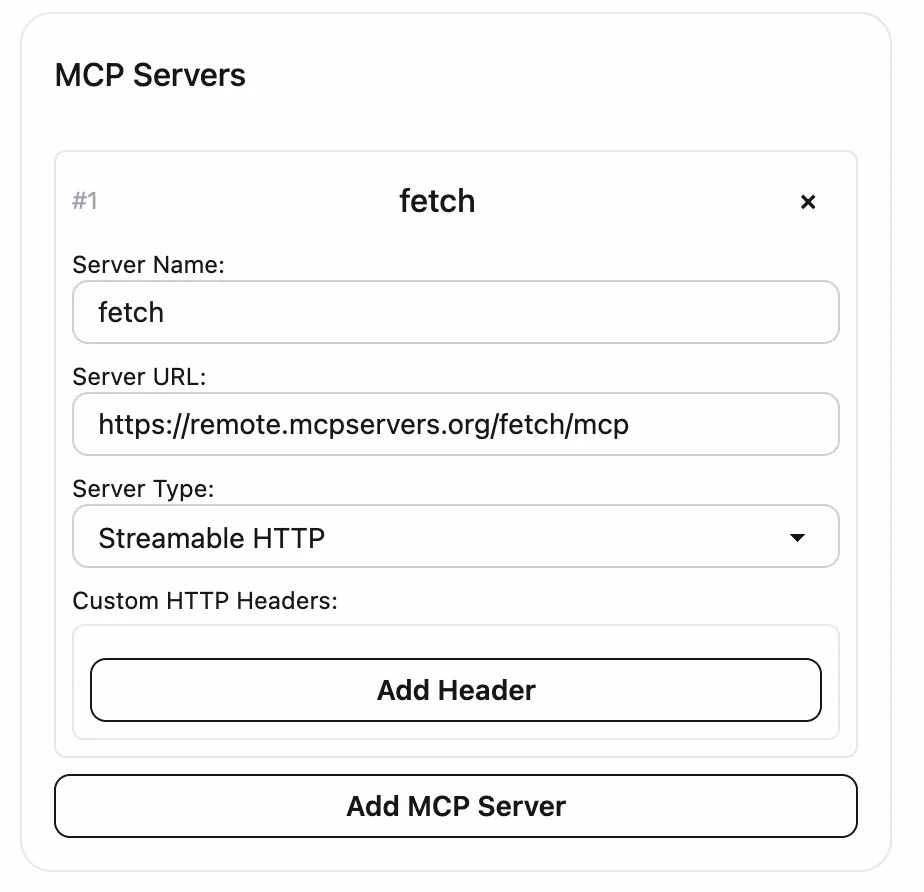
- Configuration Requirements: Each MCP server requires a name, URL, and type. Only
sseandstreamable-httpare supported. - Schema Validation: The Worker validates tool schemas one by one in
ValidateAllToolSchemas. If errors exist, all issues are aggregated and returned for easy adjustment. - Execution Fallback: Even if some MCP servers fail to connect, the system continues executing other available tools and logs warnings.
- Authentication Handling: You can configure independent headers for each MCP endpoint on the frontend, such as
Authorizationor custom tokens.
Execution Flow & Output
- Before each iteration round, the Worker tallies token usage and performs balance checks when necessary (official models trigger billing verification).
- The Agent’s reasoning, final answers, and tool calling processes are streamed back via message flow:
Agent Round nindicates the current iteration and available tool liststreamevents contain reasoning content (reasoning) and output fragments (content)- Before tool calls,
Calling tool: ...is output with parameters
- After all iterations complete, the final result is written to
$LLMAgentNodeName.result. If the output is valid JSON, the system automatically parses and stores it in context. - Other nodes can directly reference
$LLMAgent.alias.resultor$LLMAgent.alias.argsto retrieve sub-workflow data.
Common Use Cases
- Data Collection & Analysis: Combine web scraping, calculator, and md2xls to quickly generate reports.
- Automated Customer Service & Operations: Call internal knowledge base workflows based on user inquiries, then send notifications via HTTP interface.
- Content Aggregation: Connect external knowledge sources through MCP and automatically organize multi-language summaries.
- Operations Inspection: Periodically call APIs to retrieve monitoring metrics, use hash or calculator for validation, then trigger alerts.
Usage Recommendations & Best Practices
- Task Definition: Clearly describe objectives, success criteria, and output formats. Break down complex tasks into ordered lists.
- Tool Selection: Only enable necessary tools to avoid wasting tokens on irrelevant capabilities.
- Performance Optimization: Adjust
max_iterationsbased on task complexity and limit unnecessary exploratory steps in prompts. - Debugging Tips: Start with small samples, observe reasoning and tool calls streamed back each round, then gradually increase complexity.
- MCP Maintenance: Regularly verify schema and authentication configurations. When validation errors occur, prioritize resolving related tools.
By properly configuring and optimizing the LLM Agent node, you can build highly automated intelligent workflows that significantly improve team efficiency in data processing, business operations, and integrations. For more information about variable syntax, please refer to the Variable Syntax Guide.
Need a Custom AI Agent?
Custom AI agents designed for real-world business operations.
