Workflow API
FlowAI Workflow API allows you to provide your designed workflows as API services, making them easy to integrate into your applications or systems. This guide will help you understand how to publish APIs, manage API keys, and how to call workflow APIs.
Part 1: Publishing and Managing APIs
API Publishing Process
To publish a FlowAI workflow as an API, follow these steps:
- Go to the workflow editing page you want to publish
- Complete the workflow design and ensure it functions properly
- Click the Publish API button in the top function bar
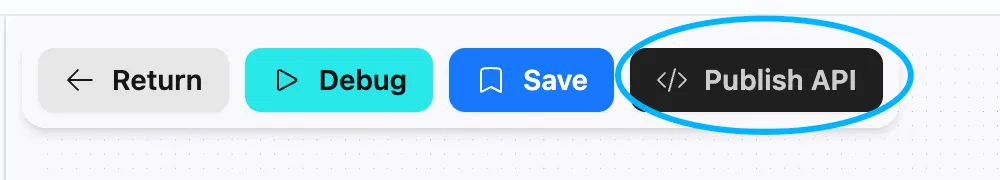
- Click the Save and Publish Current Workflow button
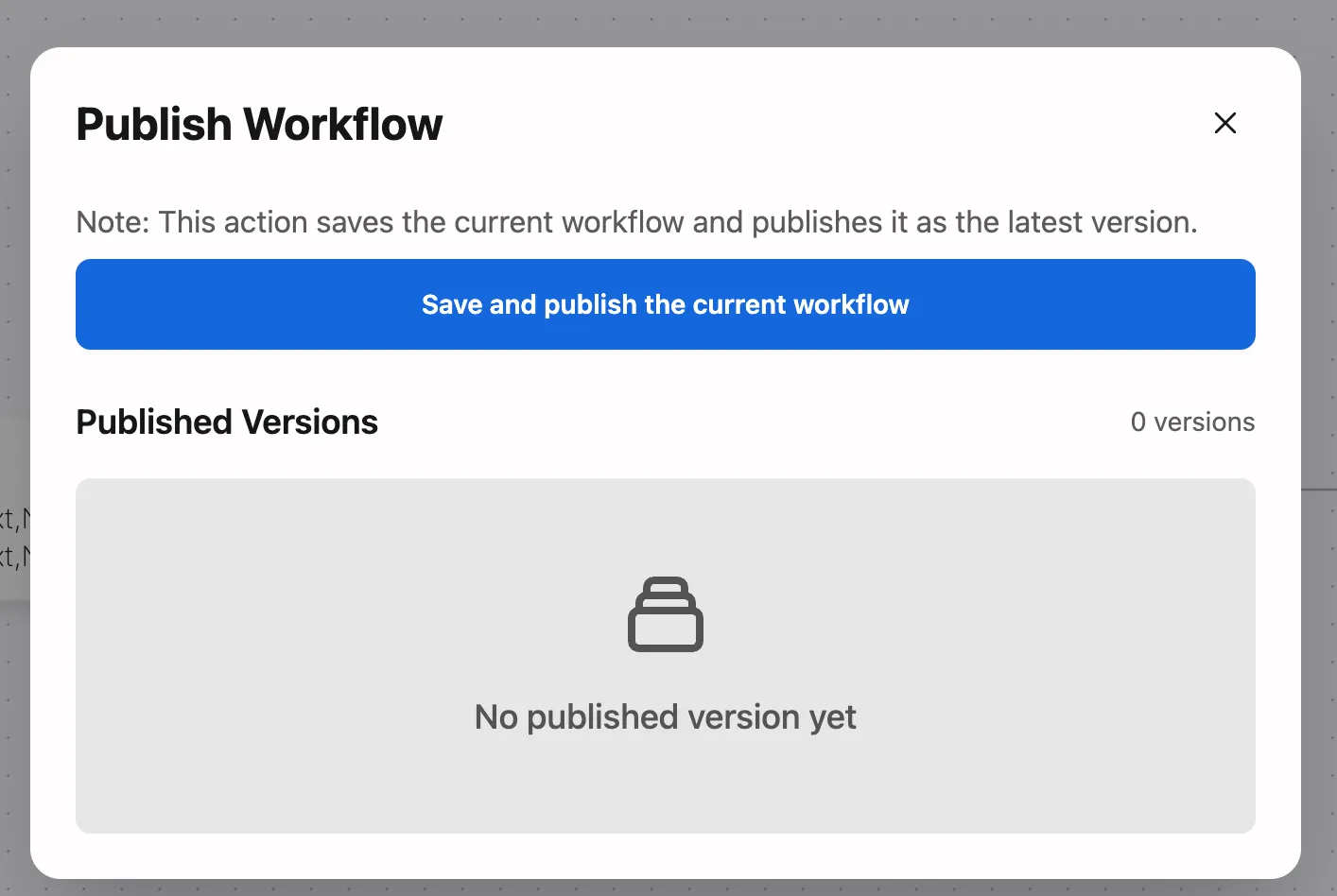
- Confirm the operation in the popup window: “This action will save the current workflow and publish it as the latest version”
- Once published successfully, your workflow can be called via API
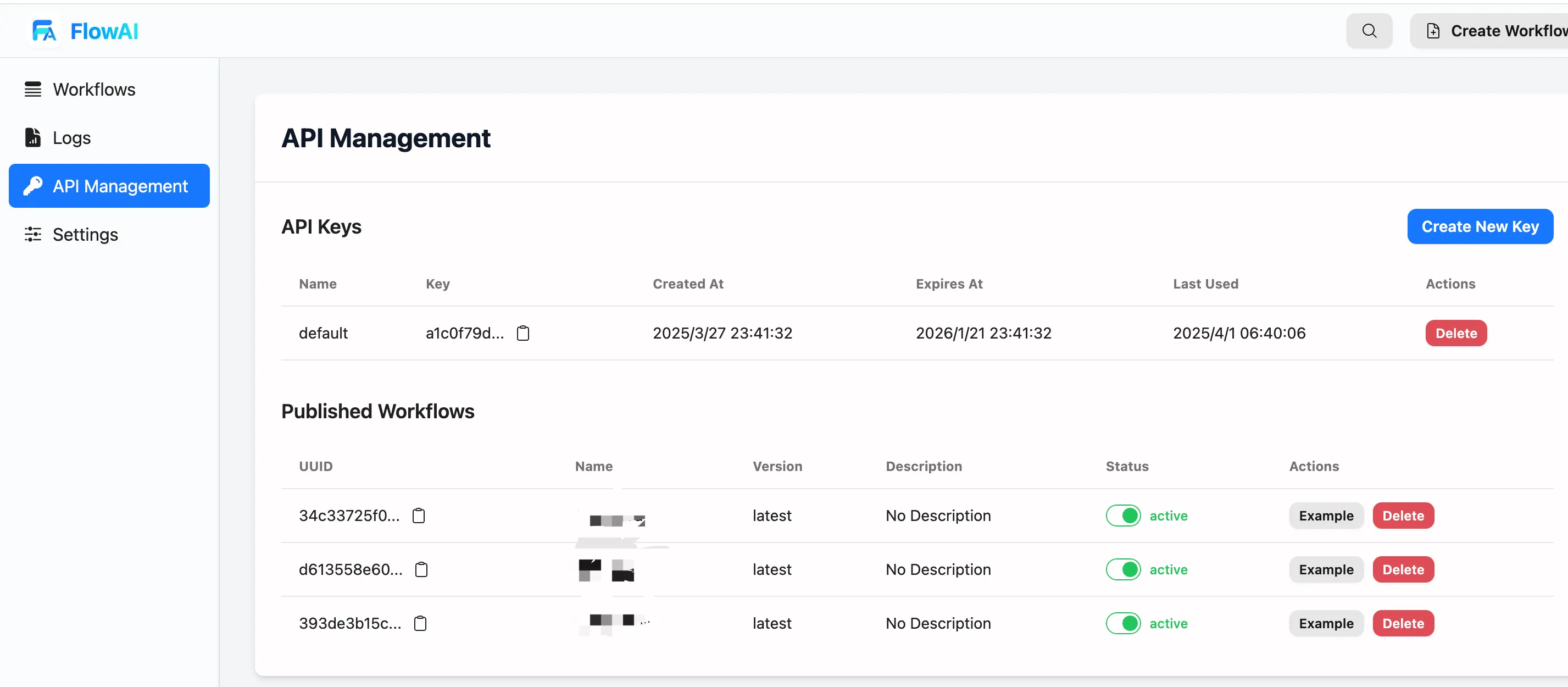
API Key Management
API keys are the credentials for calling FlowAI workflow APIs. Follow these steps to manage your API keys:
- Click the API Management option in the left navigation bar
- On the API Management page, you can:
- View existing API keys
- Create new API keys
- View the list of published workflows and their status
Important Note: When using the API feature for the first time, you need to create an API key. Click the “Create New Key” button to generate a new API key. Please keep your API key secure and do not share it in public.
Part 2: API Call Guide
Basic Call Format
FlowAI workflow API adopts a REST style. The basic call format is as follows:
curl -X POST https://flowai.cc/v1/api/workflow/run/:workflow_ID \-H 'X-API-KEY: <KEY>' \-d '{"input":<input_parameters>}'Where:
:workflow_ID: Your workflow ID (can be found on the API Management page)<KEY>: Your API key<input_parameters>: Parameter object defined by the workflow input node
Parameter Description
The main parameters for API requests include:
-
Input Parameters: Different workflows require different input parameters based on the workflow design
- Image processing workflow example:
{"input":{"url":"http://example.com/image.jpg"}} - Text processing workflow example:
{"input":{"text":"Text content to be processed"}} - Conversation workflow example:
{"input":{"input":"Are you there?"}}
- Image processing workflow example:
-
Streaming Output Parameter: Add
"stream":trueto enable streaming output- Standard call:
{"input":<input_parameters>} - Streaming call:
{"input":<input_parameters>,"stream":true}
- Standard call:
Return Format
FlowAI workflow API supports two return modes: standard output and streaming output.
1. Standard Output
In standard output mode, the API returns the result all at once after processing is complete:
Request Example:
curl -X POST https://flowai.cc/v1/api/workflow/run/:workflow_ID \-H 'X-API-KEY: <KEY>' \-d '{"input":{"input":"Are you there?"}}'Response Example:
{ "output": "Yes", "total_time": 9.316849339000001}Response field description:
output: The final output result of the workflowtotal_time: Total execution time of the workflow (seconds)
2. Streaming Output
Streaming output mode is suitable for workflows containing Large Language Models (LLM), capable of returning the processing progress and results in real-time:
Request Example:
curl -X POST https://flowai.cc/v1/api/workflow/run/:workflow_ID \-H 'X-API-KEY: <KEY>' \-d '{"input":{"input":"Are you there?"},"stream":true}'Response Example (Server-Sent Events format):
event:msgdata:{"Node":"myinput","Msg":"start","Type":"start","Data":{"input":"Are you there?"}}
event:msgdata:{"Node":"myinput","Msg":"Start node Start, type in","Type":"start_node","Data":null}
event:msgdata:{"Node":"myinput","Msg":"Finish node Start, type in","Type":"finish_node","Data":{"time_spend":0.000125251}}
event:msgdata:{"Node":"1741675999864","Msg":"Start node LLM1, type llm","Type":"start_node","Data":null}
event:streamdata:{"Content":"Yes","Node":"1741675999864","Reasoning":null}
event:streamdata:{"Content":",","Node":"1741675999864","Reasoning":null}
event:streamdata:{"Content":" I","Node":"1741675999864","Reasoning":null}
event:streamdata:{"Content":"'m","Node":"1741675999864","Reasoning":null}
event:streamdata:{"Content":" here","Node":"1741675999864","Reasoning":null}
event:streamdata:{"Content":".","Node":"1741675999864","Reasoning":null}
event:msgdata:{"Node":"1741675999864","Msg":"Finish node LLM1, type llm","Type":"finish_node","Data":{"time_spend":4.758483707}}
event:msgdata:{"Node":"1741676038250","Msg":"Start node Output 1, type out","Type":"start_node","Data":null}
event:msgdata:{"Node":"1741676038250","Msg":"Finish node Output 1, type out","Type":"finish_node","Data":{"time_spend":0.000128861}}
event:outputdata:{"output":"Yes, I'm here.","total_time":4.758748069}Part 3: Event Types and Example Applications
Streaming Output Event Types
Streaming output contains three main event types:
-
event:msg: Node running logstart: Workflow starts runningstart_node: Node starts executionfinish_node: Node execution completes, including time spent
-
event:stream: LLM streaming outputContent: Currently generated text fragmentNode: The node ID that generates the contentReasoning: Reasoning process (if applicable)
-
event:output: Final output resultoutput: Complete output contenttotal_time: Total time spent
-
event:error: Returned in case of errors
Example Application Scenarios
Through streaming output, you can build various real-time responsive applications:
- Intelligent Customer Service Bot: Display reply generation process in real-time, improving user experience
- Content Generator: Progressively display generated articles, code, or creative content
- Real-time Translation Tool: Translate as you input, reducing waiting time
- Educational Assistant Tool: Show thinking process, helping learners understand problem-solving steps
Part 4: Best Practices and FAQs
API Call Best Practices
Exception Handling
- When encountering interface errors, first check the status code:
- 401: Check if you copied the API key correctly
- 429: Rate limit triggered, take a break before trying again
- 5xx: Server issues, try again in a few minutes
- For network fluctuations, we recommend:
- Implement 3 retries with exponential backoff
- Show user-friendly prompts like “Service is temporarily unavailable, trying to reconnect”
- Categorize error logs: network issues/parameter errors/service exceptions
API Key Security Guidelines
Treat your API key like a bank card PIN:
-
Don’t hardcode keys in frontend projects, for example:
// Bad practice ❌const API_KEY = "sk-123456...";// Correct approach ✅const API_KEY = process.env.API_KEY; -
Recommend using a backend service to relay requests
-
Update keys periodically
Improving Response Speed
Optimization techniques for streaming conversation scenarios:
- Use professional SSE client libraries (such as Python’s sseclient)
- For high-frequency calls:
- Set up local caching (cache identical parameter requests for 5 minutes)
- Configure CDN acceleration for static resources
- Use leaky bucket algorithm to control request rates (e.g., no more than 20 requests per second)
Parameter Validation
Our Workflow doesn’t validate content, so ensure input content is valid before making calls.
- Format validation:
- Use whitelists for required fields
- Check email/phone formats with regular expressions
"input": {"email": "user@example.com", // regex: ^[a-zA-Z0-9._%+-]+@[a-zA-Z0-9.-]+\.[a-zA-Z]{2,}$"phone": "13800138000"} - Content filtering:
- Escape special characters (<>&, etc.)
- Filter sensitive words (political/advertising/abusive content)
- Boundary handling:
- Truncate text length (prompt for modification if exceeding 500 characters)
- Limit image size (recommended not to exceed 5MB)
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How do I get the workflow ID?
A: You can find the ID of each workflow in the published workflow list on the API Management page. You can copy the ID and call code with one click.
Q: How do I handle errors in API calls?
A: The API returns standard HTTP error codes. You should take appropriate measures based on the error code. Common errors include authentication failure (401), parameter error (400), etc.
Q: Can I use other programming languages to call the API?
A: Yes, FlowAI API is a REST API based on standard HTTP protocol and can be called using any programming language that supports HTTP requests.
